What is Elbow Pain?
Elbow pain is most frequently associated with overuse injuries, such as sprains and strains, but can also occur following injuries like fractures or dislocations. Elbow pain may cause discomfort felt in the elbow itself, or that may spread down the forearm and into the wrist. Pain may vary greatly by person and injury, ranging from a dull ache to an intense burning. In addition to pain, you may experience swelling, stiffness, and cramping. Symptoms may worsen when tightening your grip, straightening your arm, or lifting an object. Left untreated elbow injuries and pain can worsen, eventually leading to decreased range of motion, loss of strength, and decreased function of the elbow, forearm, wrist, and hand.
Understanding Elbow Anatomy
The elbow is a hinge joint that connects two bones in the forearm (the ulna and the radius), to the humerus bone in the upper arm. The ends of all three bones are cushioned by cartilage and synovial fluid, materials that create a low friction environment for the joint’s bones to move smoothly and needed to protect the bones by absorbing shock. The elbow contains two major tendons, three nerves, four main ligaments, and seven muscles. Working in tandem with its connected parts, the elbow acts as the fulcrum of the arm. It is powered mostly by the bicep muscle and uses the forearm/hand to hold, push, and carry weight. The elbow is crucial to performing everyday activities. It allows the arm to bend/straighten and for it to raise or move objects. The elbow is susceptible to stress from repetitive movements and strain from strenuous activities, making it prone to injury and the effects of overuse.
Causes of Elbow Pain
Elbow pain may be the result of a traumatic injury, a chronic condition, or simple overuse. Common causes of elbow pain include:
- Playing racquet sports, like tennis, pickleball, badminton, etc.
- Golfing, bowling, baseball, weightlifting, gymnastics, etc.
- Jobs in construction, manufacturing, cashiering, cooking, or computer work
- Sewing, knitting, crafting, gardening
- An acute Injury from hitting the outside of the elbow

Elbow Pain Conditions We Treat
Armworks Hand Therapists have extensive knowledge and training in rehabilitating elbow injuries. They regularly provide lasting effective elbow pain therapy for:
- Tennis elbow and Golfers’ elbow
- Elbow dislocation
- Ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) injury
- Flexor tendinitis
- Bursitis
- Valgus extension overload (VEO)
- Olecranon stress fracture
- Ulnar neuritis
- Cubital tunnel syndrome
- Arthritis
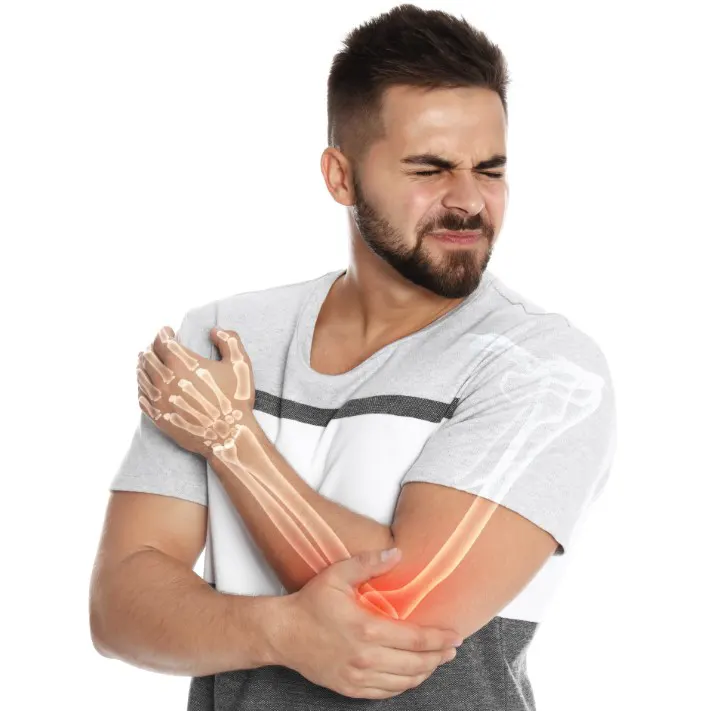
Elbow Pain Treatment
Therapy for elbow injuries is not a one-size fits all solution. Armworks Hand Therapists specialize exclusively in elbow, wrist and hand conditions. At your first appointment, your hand therapist will perform a professional evaluation to assess your injury or condition. They will then develop a customized treatment plan to best meet your individual recovery needs. Your elbow pain treatment may include:
- Treatment/instructions to reduce inflammation
- Manual Therapy
- Splinting for the elbow and/or wrist
- In clinic and at home exercise programs
- Education on correct use of your arm and injury prevention

Frequently Asked Questions
-
How will my elbow pain symptoms progress?
The typical progression of symptoms starts with an occasional dull ache or brief sharp pains in the elbow which can then lead to more frequent occurrences or longer periods of pain. Eventually you begin to avoid using your arm which can cause weakness and loss of motion.
-
When should I seek treatment for elbow pain?
In short, the earlier you can start therapy for elbow pain or an elbow injury, the better. The most common thing hand therapists hear from patients is, “I just thought it would go away so I waited to call,” but waiting actually causes the recovery period to last much longer.
-
How long will elbow therapy typically last?
The recovery time is typically shorter the sooner you can start therapy after your symptoms begin. A normal amount of recovery for an elbow issue is 2-4 weeks if starting therapy early and 4-8 weeks if starting later.
-
When can I return to work after an elbow injury?
Returning to work after an elbow injury depends on what type of job you do and how much you use your elbows in your job. Believe it or not, computer-based jobs often put the most stress on your elbows. By making some simple changes to your computer habits, you often do not need to miss very much work after an elbow injury.
-
When can I return to playing sports after an elbow injury?
After an elbow injury, returning to sports that require throwing (like baseball or bowling) are going to take longer to return to than ones like running or cycling. Sports that involve holding a racquet or club (like tennis, pickleball, or golf) require a longer period of rest too. Expected healing timelines for elbow pain are around 2-4 weeks if starting therapy early, and around 4-8 weeks if starting therapy later.
-
Does Armworks take my insurance?
Here is a list of the insurance plans accepted by SportsCare Physical Therapy and Armworks Hand Therapy. If you are unsure of your coverage or if your plan is accepted, please contact one of our offices. We are happy to assist you in learning about your benefits.
-
Where is Armworks located?
Armworks Hand Therapy has offices in Gresham, NE Portland, Clackamas, Beaverton, and Lake Oswego. For location specific contact information click here.
